
In this guide, we will walk through exposing a local PostgreSQL instance withngrok. This method allows you to quickly test and analyze the behavior of PostgreSQL with data platforms likeMeroxa.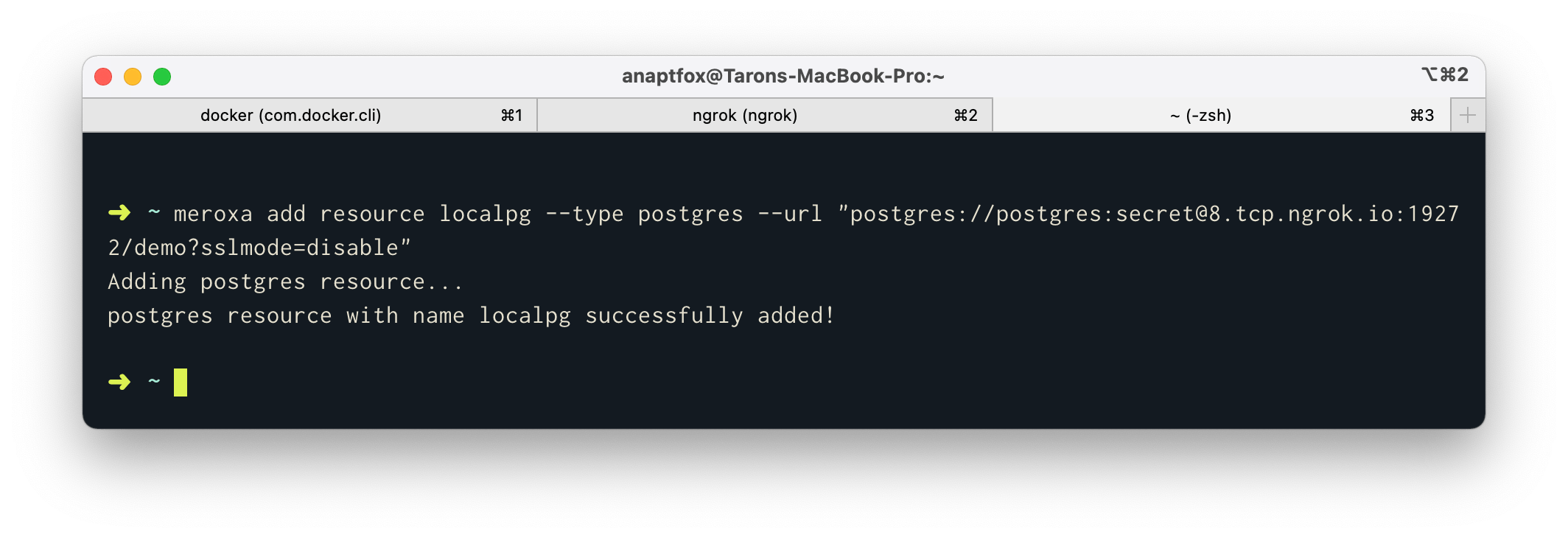 For this example, we are going to use ngrok. ngrok exposes local servers behind NATs and firewalls to the public internet over secure tunnels.
For this example, we are going to use ngrok. ngrok exposes local servers behind NATs and firewalls to the public internet over secure tunnels.
Let's begin.
Step One: Running PostgreSQL Locally
Before we begin, you'll need to havePostgreSQL installed and running locally. The easiest and quickest way usingDocker:
$ docker run --rm -p 5432:5432 -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=secret -e POSTGRES_DB=demo postgres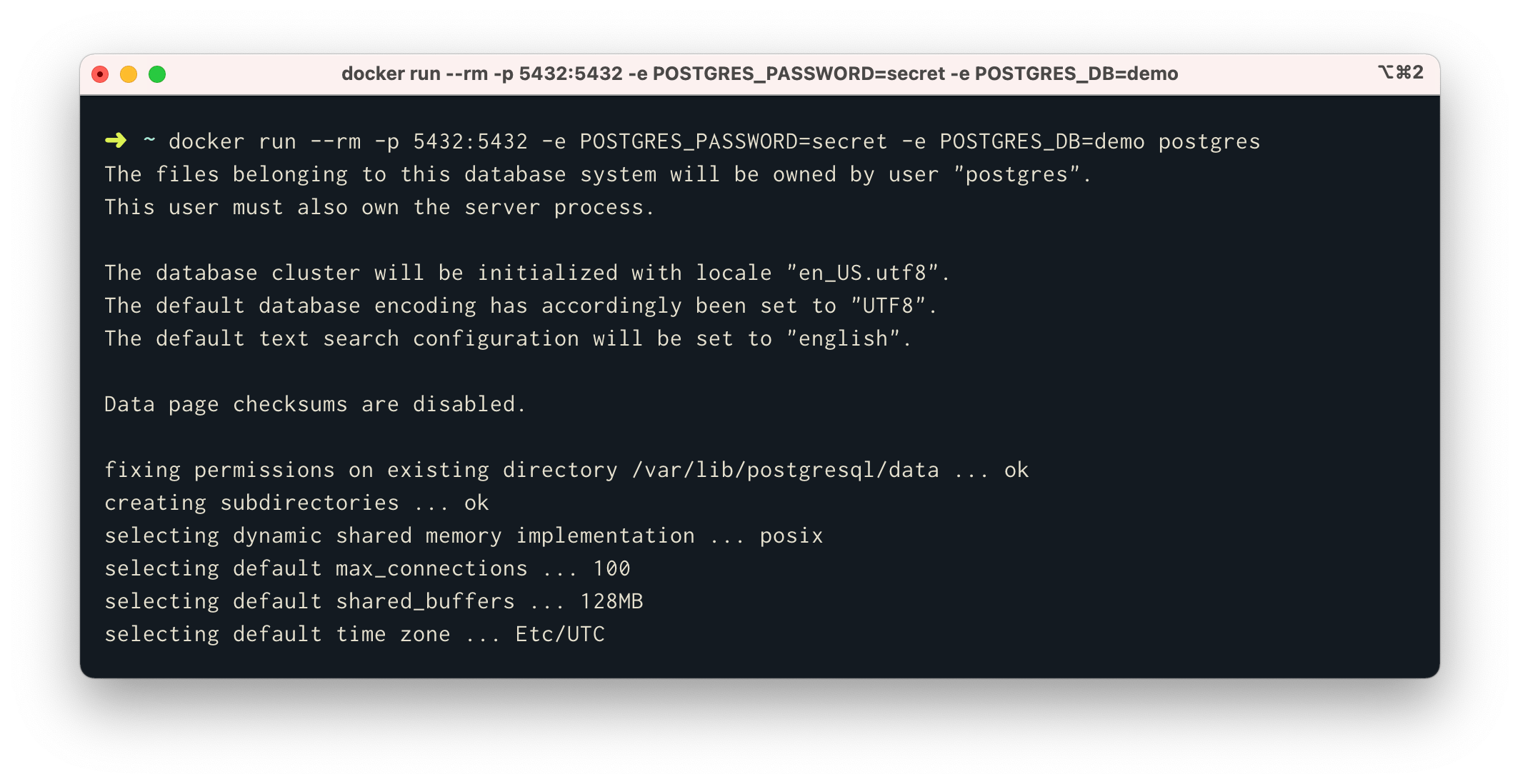
For more details on configuration, seepostgres on Docker Hub.
Now
Now that PostgreSQL is running on port5432, you can connect to the local databaseoutside of the container usingpsql :
$ psql -U postgres -h localhost -p 5432 postgresStep Two: Running ngrok and Exposing PostgreSQL
Next, we can create a tunnel using ngrok and expose the locally running database.
First, you'll need todownload and install ngrok, andcreate an account. Then, you can start the tunnel by running the following:
$ ngrok tcp 5432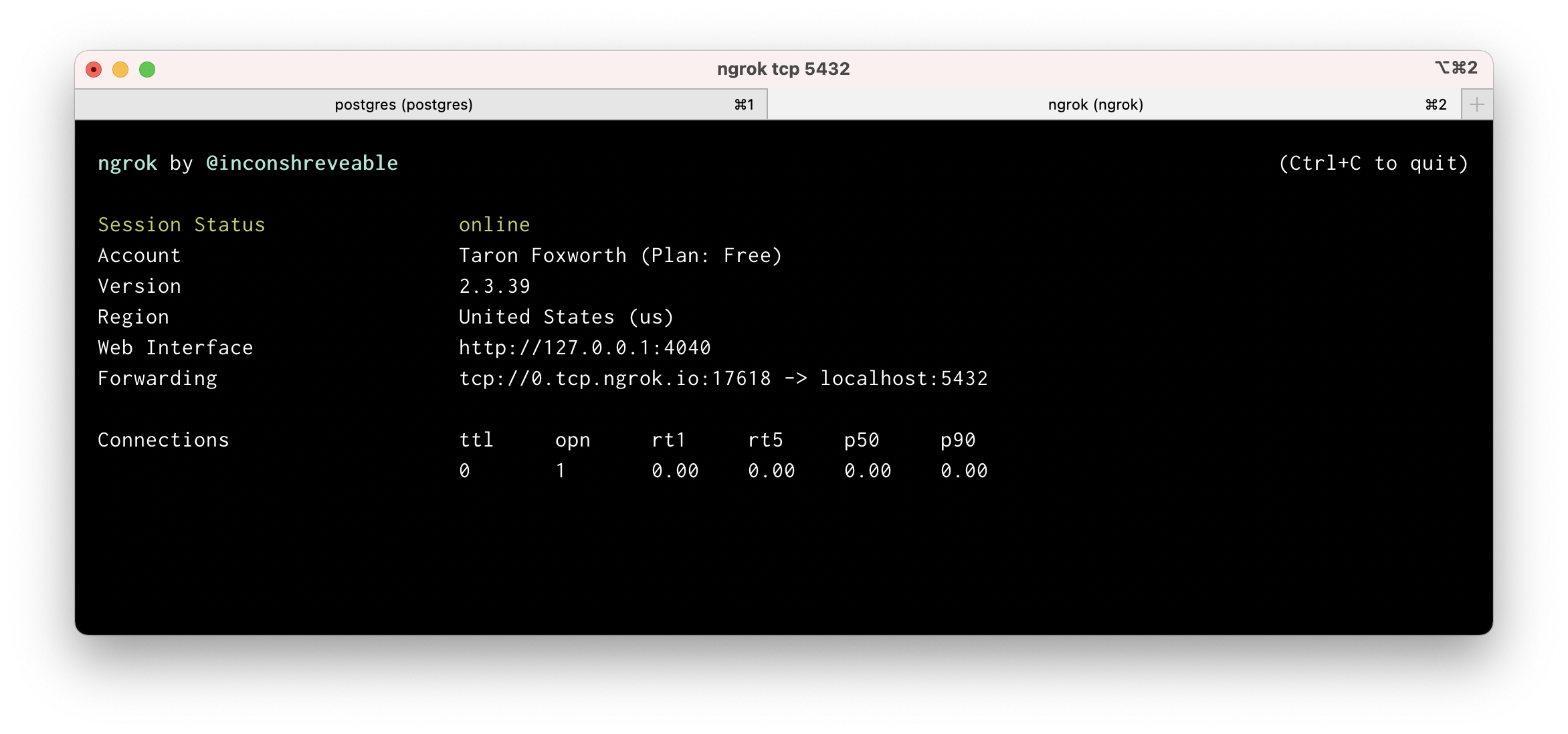
For more information, seengrok tcp.
Note: You'll need to create an ngrok account to use tcp forwarding.
Step Three: Connecting to PostgreSQL
Now that PostgreSQLand ngrok are running, you can connect to the publically exposed database usingpsql:
$ psql -h 0.tcp.ngrok.io -p 17618 -U postgres -d postgres>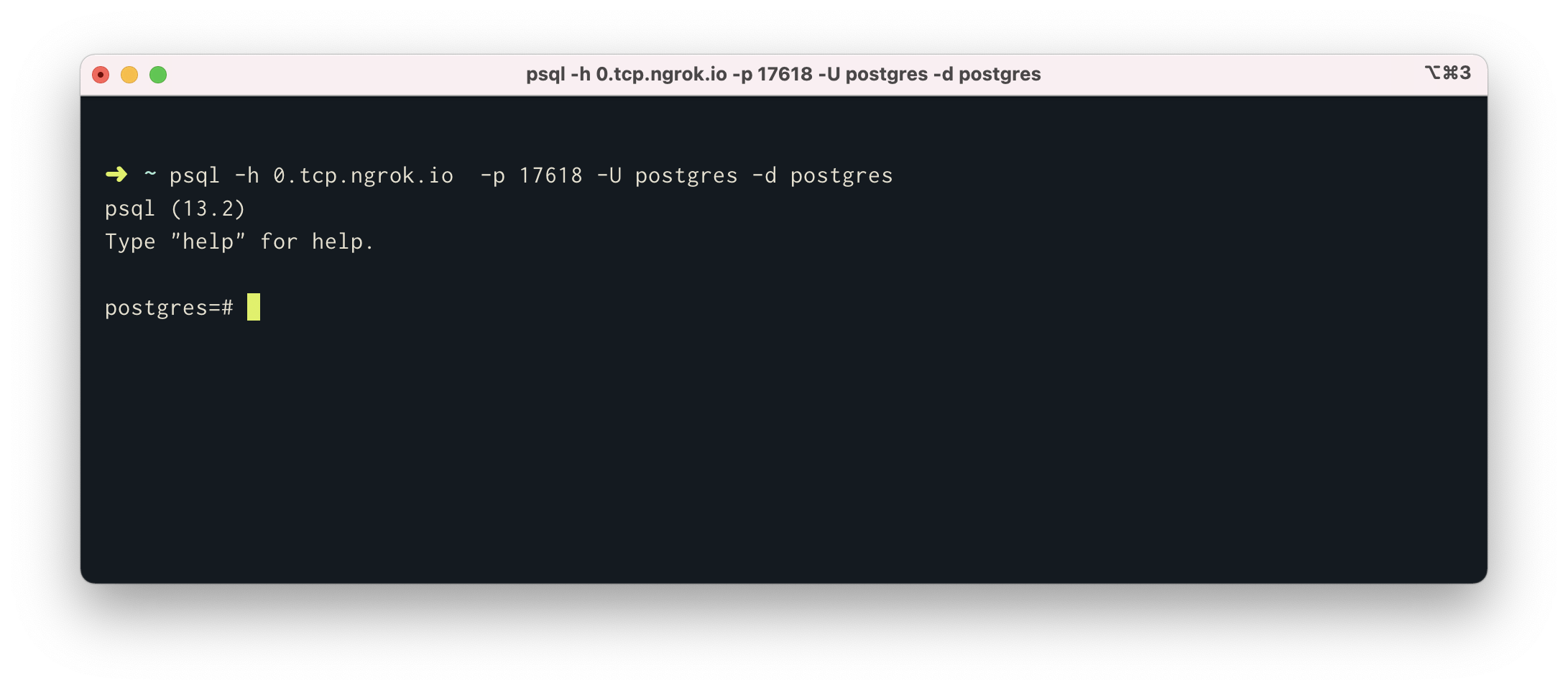 That's it! You can now connect to your local instance over the internet.
That's it! You can now connect to your local instance over the internet.
What's next?
This method super helpful to quickly test and analyze behavior using PostgreSQL with cloud services. For example, you can add the local PostgreSQL to Meroxa:
$ meroxa resource create localpg --type postgres --url "postgres://postgres:secret@8.tcp.ngrok.io:19272/demo?sslmode=disable"Note: Since our database is local, SSL is not enabled by default. To connect, you'll need to append?sslmode=disable to the PostgreSQL connection URL.
By adding it as a Meroxa Resource, you can easily capture real-time CDC events for every insert, update, delete operation from a local PostgreSQL table. For more, seePostgreSQL Resource Documentation.
Helpful Resources:
I can't wait to see what you build 🚀.